Wednesday, August 31, 2011
Using quarantine as a barrier to trade
I have been meaning to write about using quarantine as a barrier to trade since Queensland’s banana crop was destroyed by cyclone Yasi last summer and prices at the supermarket shelf hit $14/kilo and more. It seems that leading economist Saul Eslake, and economist turned politician Andrew Leigh, have done the job of deciphering genuine concerns over importing disease, and rent seeking by protected producers.
Let us start with what Andrew had to say.
In fact, just about every trade barrier can be rewritten as a quarantine rule or a consumer protection law. Suppose Californian wine producers are complaining about competition from French Bordeaux. Left unchecked, US authorities could simply raise health concerns about Phylloxera, and ban French wines on quarantine grounds. Or imagine that British carmakers are struggling to compete with Malaysian hatchbacks. Without any international guidelines, there would be nothing to stop the UK from banning Malaysian small cars for reasons of safety.
To prevent competition laws and environmental rules from being used as backdoor protectionism, the WTO has two new treaties that require health, consumer and environmental regulations to be scientifically based. National regulations cannot discriminate against particular countries, and must not impede trade any more than necessary.
If a WTO member thinks that another country is breaking the global trade rules, it can take a case to the dispute panel. Australia has complained to the WTO on seven occasions (against the European Union, Hungary, India, Korea, and the United States). We’ve won five of these cases, including decisions in favour of our beef exporters to Korea and our lamb exporters to the US.
On the flipside, we’ve had ten cases brought against us (by Canada, the EU, New Zealand, the Philippines, Switzerland, and the US). We’ve lost three of these cases, including the New Zealand apples decision (the other two losses related to imports of salmon and automotive leather).
Andrew makes the solid points that quarantine and consumer protection is ‘back-door’ protectionism, and gives a good overview of the international legal framework around trade.
Saul Eslake takes different approach by discussing the price impacts on domestic consumers from this type of protection. He also highlighted that in the wake of cyclone Yasi, high banana prices were only helping banana growers whose crops weren’t destroyed, not those who actually lost their crops from the cyclone.
On the matter of importing diseases, he makes a point I have argued to many people in the past. How would diseases go from boxed-up fruit and vegetables arriving in city ports out to farms? How high is that risk? In Eslake’s words-
If bananas and other fruit or vegetables are imported into southern ports, such as Melbourne, Adelaide or Sydney, and are subject upon arrival to appropriate inspections, they are no more likely to spread diseases damaging to Australia's banana industry than the importation of cooked and packaged Canadian salmon has done to Tasmania's salmon industry (another example of protectionism masquerading as ''biosecurity'' where, unusually, commonsense and the interests of consumers ultimately prevailed).
To me the irony of the situation is that most of the crops now requiring protection from foreign pests are imported themselves, and could arguably be classified by an environmentalist as a foreign pest.
The other irony is that the countries that do have these diseases are also exporters and can produce the crop much cheaper than us.
The logical person would ask whether the potential costs from the pest or disease are greater than the benefits derived by consumers from cheaper food? If yes, then we should keep the quarantine restrictions. If no, we should drop them.
I am not trying to say here that all quarantine rules necessarily have greater benefits than there costs. But we have lost 3 out of ten cases brought against us by other WTO member, so if 30% of the quarantine rules can be dropped because their costs outweigh the benefits, that would be good for everyone in the long run.
Property industry propaganda knows no bounds (+market update)
The above video is from Bernard Salt's presentation at the 2011 Property Council of Australia's 'Geared for Growth' Congress recently held in Darwin. In the presentation he calls for the construction, property and banking sectors to combine forces to fund a lobby group to infiltrate social media, and blogs in particular, to counter the negative sentiment that is leading property markets into the doldrums.
Astonishing. As fellow blogger Tony Harris notes in his detailed analysis of the video -
Who are you really chatting with, when you post on that property forum or blog? A regular person like yourself, or a paid spruiker, funded by the real estate industry?
Around the 8 minute mark Salt discusses the hostile reception to an article he published online spruiking the virtues of growth (population growth I assume). He had this to say about the reader comments -
Not one person in 230 put a reasoned, balanced, measured counter-response. I want to see someone actually in there. Every time you don't respond, negative sentiment extends just that bit further across middle Australia.
After pointing the finger at 'negative sentiment' as the cause of the current economic slowdown he goes on to suggest his solution (screenshot below quote)
I want to see someone, somebody, some group of people, counter the negativism in all theatres, social media, twitter, the blogosphere, seek out and, not destroy, seek out and balance every extreme view - take the fight to them. Sitting back is not an option. I do understand that individuals cannot do this, but surely there is a way to fund a group to do it on your behalf. This it not a pitch for me, but I am surely happy to advise on how to set it up.
What is ironic, to me, is that the property and construction industry lobby groups might actually go for Salt's big idea, as if a few blog comments and Facebook pokes can stop Australia following the rest of the world to its economic destiny.
Salt suggests perhaps they need an (another) 'independent' pro-growth, pro-development sentiment-generating lobby group which could be funded by the BCA, the Property Council of Australian and of all things, the Australian Bankers Association.
The banks would probably join because of the negative sentiment towards them at the moment. Salt comments -
The idea that banks should not get a fair return on their investment is bizarre. We've got this disconnect in Australia between the way we want to live, our superannuation, and our objection to every development, to anyone making a profit.
I for one can understand the concern over bank profits. After all, bank executives and shareholders seem happy to take the profits while taxpayers insure the losses. All the while they have played a key role in the property bubble with their declining lending standards.
Face it Bernard, you can't stop the realities of economics and finance by tweeting 140 characters or less.
And speaking of the realities of economics and finance, that national house price slide accelerated in July according to Rismark. Note that in Perth and Brisbane prices have been falling for more than 12 months, so the falls from peak are much higher than these figures show. From my reading of old data I could guess that Brisbane prices are down about 11% over 15months.
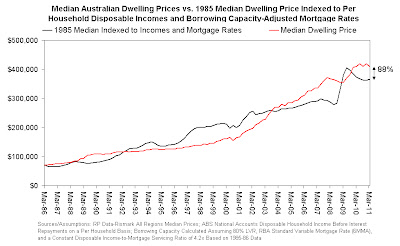
Coinciding with their press release was the most bizarre property analysis yet from Rismark data guru Chris Joye. Joye's analysis of late has been squarely aimed at providing evidence that current house prices are supported by 'economic fundamentals', including the once-off adjustment in interest rates, higher household incomes, and so on.
This time he mightily proclaims to-
... show that by indexing up median Australian dwelling prices by per capita disposable incomes and changes in borrowing capacity (as determined by mortgage rates) one can account for around 90 per cent of the rise in Australian housing costs over the last two and a half decades
Which I guess is a roundabout way of saying prices are 10% overvalued at most. Joye presents the following graph to demonstrate his result, but I can't help wondering why he chose 1986 as a start date. Had he chosen 1990 as the start date he could have shown that houses are undervalued according to his fundamentals, but had he chosen 1998 as his start date, his fundamentals would have only explained about 50% of the house price. Most bizarre.
As I have said before, yes lower interest rates and higher incomes do explain some of the growth, but only about 70% of today's prices. There is also always the risk that incomes will fall as house prices fall, but always the chance that mortgage interest rates will drop to slow any accelerated price declines. The downside risks are far greater than any upside potential in the housing market at the moment, and I do wonder why Chris seems so keen to give the impression that this is not the case.
In other housing news today, Leith van Onselen from the Macrobears superblog [just kidding guys ;-)] has explained in detail in this SMH article why the RBA appears to underplay the risks, and underestimate the size of, the bubble in the Australian housing market. Simply, they use a measure of average household income about 33% higher than actual household incomes. Who would have guessed that the average household disposable income was actually $74,360, and the median just $60,580 - not the $100,000+ used in the RBA's analysis? Not the RBA it seems. Oops.
Finally, I stumbled across this article (somewhat belatedly) arguing essentially that housing supply is driven by housing turnover, and is completely unrelated to price. This might come as a shock to the 'elastify the supply side' believers. It is also odd that mostly valuers and honest property developers seem to be the few groups who argue this concept.
Let me give a few practical examples – First, imagine the construction of a residential unit block – the developer, because of cash flow or financier requirements, needs to sell a large proportion of the development “off-the-plan”.
Simply, until pre-completion sales are locked away nothing gets built.
Second example - for house and land packages in new estates, buyers purchase the block of land first and arrange the construction afterwards. In either case there is no “build it and they will come”. It is the demand that sets the pace.
Which is what I have tried to say for some time, and said back in April like this -
The rate of land and housing supply is determined by the rate of sales of new stock (known as the absorption rate). It has nothing to do with the rate of development approvals or even the price level.
The rate of land and housing supply is determined by the rate of sales of new stock (known as the absorption rate). It has nothing to do with the rate of development approvals or even the price level.
Monday, August 29, 2011
Tobin tax for Australia?
But I see offhand no other way to prevent financial transactions disguised as trade
The tax on foreign exchange transactions was devised to cushion exchange rate fluctuations. The idea is very simple: at each exchange of a currency into another a small tax would be levied - let's say, 0.5% of the volume of the transaction. This dissuades speculators as many investors invest their money in foreign exchange on a very short-term basis. If this money is suddenly withdrawn, countries have to drastically increase interest rates for their currency to still be attractive. But high interest is often disastrous for a national economy, as the nineties' crises in Mexico, Southeast Asia and Russia have proven. My tax would return some margin of manoeuvre to issuing banks in small countries and would be a measure of opposition to the dictate of the financial markets. (here)
A 1978 article where Tobin reflects on global monetary reform is here, and well worth a read. The relevance to Australia in 2011 is quite clear when he says -
National economies and national governments are not capable of adjusting to massive movements of funds across the foreign exhcanges, without real hardship and without significant sacrifice of the objective of national economic policy with respect to employment, output and inflation.
National economies and national governments are not capable of adjusting to massive movements of funds across the foreign exhcanges, without real hardship and without significant sacrifice of the objective of national economic policy with respect to employment, output and inflation.
While Tobin originally suggested that all countries cooperate to implement a standard tax rate, with revenues raised pooled centrally, the idea is equally valid for a single currency-issuing nation to tax conversions of its own currency.
The logic behind the tax is quite sound. An influx of foreign funds only provides domestic benefits when it backs real investment in productive enterprise. And investing in a real business takes time. As Canadian economist Rodney Schmidt noted in 1994
In two-thirds of all the outright forward and [currency] swap transactions, the money moved into another currency for fewer than seven days. In only 1 per cent did the money stay for as long as one year
The logic behind the tax is quite sound. An influx of foreign funds only provides domestic benefits when it backs real investment in productive enterprise. And investing in a real business takes time. As Canadian economist Rodney Schmidt noted in 1994
In two-thirds of all the outright forward and [currency] swap transactions, the money moved into another currency for fewer than seven days. In only 1 per cent did the money stay for as long as one year
A currency exchange tax reduces the gains from short term currency trades, and for a single country, allows them to reduce distortionary taxes elsewhere in the economy leading to productivity benefits. It also means there is a strong incentive for national savings to be invested locally, and a cost to banks seeking offshore funding to support their capital requirements. It also provides local governments some degree of control over their economy, rather than being at the mercy of global conditions. These are all good things.
Of course, like any tax, the risk is that governments simply spend this extra revenue unproductively and do not reduce distortionary taxes elsewhere in the economy, which greatly reduces its potential benefits.
In 2009 Brazil implemented a similar financial transaction tax regime that applies to foreign investment in stocks and fixed-income securities at a rate of 2%. And it seemed to work -
Brazil's currency and stocks fell sharply yesterday after the government imposed a 2 per cent tax on foreign portfolio investments to stem the rapid rise of its exchange rate.
But only for a while. The chart below shows the Real regained its strength fairly quickly.
Of course, like any tax, the risk is that governments simply spend this extra revenue unproductively and do not reduce distortionary taxes elsewhere in the economy, which greatly reduces its potential benefits.
In 2009 Brazil implemented a similar financial transaction tax regime that applies to foreign investment in stocks and fixed-income securities at a rate of 2%. And it seemed to work -
Brazil's currency and stocks fell sharply yesterday after the government imposed a 2 per cent tax on foreign portfolio investments to stem the rapid rise of its exchange rate.
But only for a while. The chart below shows the Real regained its strength fairly quickly.
(This is not to be confused with Brazil's former Contribuição Provisória sobre Movimentação ou Transmissão de Valores e de Créditos e Direitos de Natureza Financeira, or CPMF, which was a transaction tax levied at 0.038% on all bank transactions from 1993 till the end of 2007)
Of course the empirical macroeconomic problem arises once again here - would the Real have been even stronger if not for the tax? Who knows? My gut feeling is that because economic agents adapt very quickly to new taxes, their offsetting behaviour can greatly reduce the intended effect.
Since that time, the global battle to devalue domestic currency has resulted in many calls to implement Tobin taxes, from the British Prime Minister to the French President, with all political leaders seeking input from the IMF. The IMF is now coming around to the idea (recently releasing this working paper), and with DSK's likely replacement Christine Lagarde being a fan (here), chances have improved that this tax will be supported globally.
There is even strong support from the economics profession, with1000 economists writing a letter in support of the idea earlier this year. A good summary of the breadth of support (and not) for such a tax is here. Even economists at the Australian Treasury are talking about it.
The cynic in me says that such a tax is unlikely because those who benefit from fast and cheap currency exchange are those with the most money, while those who bear the burden of a high domestic currency are usually the workers in marginally competitive industries.
For Australia I see only upsides to this tax. A lower Australian dollar and reduced foreign investment will help to slowly rebalance our economy to become more diversified and stable again. While the Henry Tax Review overlooked this type of tax, at least we have a backdrop of tax reform to accompany a Tobin tax.
The outcome of this political battle with the global financial elite is anyone's guess.
Sunday, August 28, 2011
Anthropologist's view on debt and money
Over at Naked Capitalism is a fantastic interview with David Graeber, author of Debt: The First 5,000 years. The most intersting point for me is that economists just assumed that since money is currently primarily used to estimate exchange value, that this is the historical reason for the existence of money. While this view of money is often a workable assumption, the deeper social issues surrounding money become easily overlooked when you perceive money primarily as a means of exchange, and ignore the role of debt anf conflict as the tru origins of money.
An excerpt is below, and the full interview is worth reading, especially for those curious about Chartalism, Biblical debt jubilees and so on.
Philip Pilkington: Let’s begin. Most economists claim that money was invented to replace the barter system. But you’ve found something quite different, am I correct?
David Graeber: Yes there’s a standard story we’re all taught, a ‘once upon a time’ — it’s a fairy tale.
It really deserves no other introduction: according to this theory all transactions were by barter. “Tell you what, I’ll give you twenty chickens for that cow.” Or three arrow-heads for that beaver pelt or what-have-you. This created inconveniences, because maybe your neighbor doesn’t need chickens right now, so you have to invent money.
The story goes back at least to Adam Smith and in its own way it’s the founding myth of economics. Now, I’m an anthropologist and we anthropologists have long known this is a myth simply because if there were places where everyday transactions took the form of: “I’ll give you twenty chickens for that cow,” we’d have found one or two by now. After all people have been looking since 1776, when the Wealth of Nations first came out. But if you think about it for just a second, it’s hardly surprising that we haven’t found anything.
Think about what they’re saying here – basically: that a bunch of Neolithic farmers in a village somewhere, or Native Americans or whatever, will be engaging in transactions only through the spot trade. So, if your neighbor doesn’t have what you want right now, no big deal. Obviously what would really happen, and this is what anthropologists observe when neighbors do engage in something like exchange with each other, if you want your neighbor’s cow, you’d say, “wow, nice cow” and he’d say “you like it? Take it!” – and now you owe him one. Quite often people don’t even engage in exchange at all – if they were real Iroquois or other Native Americans, for example, all such things would probably be allocated by women’s councils.
So the real question is not how does barter generate some sort of medium of exchange, that then becomes money, but rather, how does that broad sense of ‘I owe you one’ turn into a precise system of measurement – that is: money as a unit of account?
By the time the curtain goes up on the historical record in ancient Mesopotamia, around 3200 BC, it’s already happened. There’s an elaborate system of money of account and complex credit systems. (Money as medium of exchange or as a standardized circulating units of gold, silver, bronze or whatever, only comes much later.)
So really, rather than the standard story – first there’s barter, then money, then finally credit comes out of that – if anything its precisely the other way around. Credit and debt comes first, then coinage emerges thousands of years later and then, when you do find “I’ll give you twenty chickens for that cow” type of barter systems, it’s usually when there used to be cash markets, but for some reason – as in Russia, for example, in 1998 – the currency collapses or disappears.
David Graeber: Yes there’s a standard story we’re all taught, a ‘once upon a time’ — it’s a fairy tale.
It really deserves no other introduction: according to this theory all transactions were by barter. “Tell you what, I’ll give you twenty chickens for that cow.” Or three arrow-heads for that beaver pelt or what-have-you. This created inconveniences, because maybe your neighbor doesn’t need chickens right now, so you have to invent money.
The story goes back at least to Adam Smith and in its own way it’s the founding myth of economics. Now, I’m an anthropologist and we anthropologists have long known this is a myth simply because if there were places where everyday transactions took the form of: “I’ll give you twenty chickens for that cow,” we’d have found one or two by now. After all people have been looking since 1776, when the Wealth of Nations first came out. But if you think about it for just a second, it’s hardly surprising that we haven’t found anything.
Think about what they’re saying here – basically: that a bunch of Neolithic farmers in a village somewhere, or Native Americans or whatever, will be engaging in transactions only through the spot trade. So, if your neighbor doesn’t have what you want right now, no big deal. Obviously what would really happen, and this is what anthropologists observe when neighbors do engage in something like exchange with each other, if you want your neighbor’s cow, you’d say, “wow, nice cow” and he’d say “you like it? Take it!” – and now you owe him one. Quite often people don’t even engage in exchange at all – if they were real Iroquois or other Native Americans, for example, all such things would probably be allocated by women’s councils.
So the real question is not how does barter generate some sort of medium of exchange, that then becomes money, but rather, how does that broad sense of ‘I owe you one’ turn into a precise system of measurement – that is: money as a unit of account?
By the time the curtain goes up on the historical record in ancient Mesopotamia, around 3200 BC, it’s already happened. There’s an elaborate system of money of account and complex credit systems. (Money as medium of exchange or as a standardized circulating units of gold, silver, bronze or whatever, only comes much later.)
So really, rather than the standard story – first there’s barter, then money, then finally credit comes out of that – if anything its precisely the other way around. Credit and debt comes first, then coinage emerges thousands of years later and then, when you do find “I’ll give you twenty chickens for that cow” type of barter systems, it’s usually when there used to be cash markets, but for some reason – as in Russia, for example, in 1998 – the currency collapses or disappears.
Thursday, August 25, 2011
Not so random links, comments and quotes
Law of demand holds
Bust fares go up, patronage goes down. A lesson for policy makers about defining their outcomes better – do they want cost recovery for transport (higher fares, lower usage), or are they willing to subsidise public transport to save costs of maintaining the road system?
Algorithms rule our lives
The algorithms of Wall Street may be the cyber-equivalent of the 80s yuppie...
The question for the economist is not whether there are downsides to this infiltration, but whether the costs outweigh the benefits. I am pretty sure that is not the case yet – after all, algorithms are written by humans, redesigned by humans, and often ignored by humans.
Culture -
The Misconception: You celebrate diversity and respect others’ points of view.
The Truth: You are driven to create and form groups and then believe others are wrong just because they are others.
If patents over software are a bad idea, why not all patents?
This article argues that companies find it more attractive to make money suing each other for infringement than actually making things.
The question for society is whether innovations would occur at close to the same level without patents? My personal view is that they would, and that a possible first mover advantage would be reward enough. A short, but very useful, free online textbook on the economics of patents and copyright is here.
Apple iPad patent fiasco
Free trade in apples, finally?
As I said before with food import restrictions, if prices are set by global markets, domestic buyers cannot buy at prices below the export market price - although they could perhaps be higher.
Essentially, by protecting our producers from import competition we are paying HIGHER prices for Australian food than foreigners are paying for Australian food.
Of course apple growers will whinge, but they will adjust over time, and in reality, their incomes have been protected for a long time anyway.
Warren Buffet supporters in France - the rich want to be taxed more
Quotes -
Graveyard market - buyers don't want in, sellers can't get out (ht: doomsday_trader)
After all, statistics are like bikinis. What they reveal is interesting, but what they conceal is more important (ht: John Booth)
If an Axe is being ground, cluelessness will follow naturally. I used to be an ideologue and as I think back on my unreflective self, I remember that I just chose to devote all my mental energy to what I wanted to believe and none to what I didn't want to believe and the result was I appeared clueless, sometimes intentionally clueless (ht: anon)
The lesson of Alaska is never give away land, even when it is seemingly worthless (ht: M)
Bust fares go up, patronage goes down. A lesson for policy makers about defining their outcomes better – do they want cost recovery for transport (higher fares, lower usage), or are they willing to subsidise public transport to save costs of maintaining the road system?
Algorithms rule our lives
The algorithms of Wall Street may be the cyber-equivalent of the 80s yuppie...
The question for the economist is not whether there are downsides to this infiltration, but whether the costs outweigh the benefits. I am pretty sure that is not the case yet – after all, algorithms are written by humans, redesigned by humans, and often ignored by humans.
Culture -
The Misconception: You celebrate diversity and respect others’ points of view.
The Truth: You are driven to create and form groups and then believe others are wrong just because they are others.
If patents over software are a bad idea, why not all patents?
This article argues that companies find it more attractive to make money suing each other for infringement than actually making things.
The question for society is whether innovations would occur at close to the same level without patents? My personal view is that they would, and that a possible first mover advantage would be reward enough. A short, but very useful, free online textbook on the economics of patents and copyright is here.
Apple iPad patent fiasco
Free trade in apples, finally?
As I said before with food import restrictions, if prices are set by global markets, domestic buyers cannot buy at prices below the export market price - although they could perhaps be higher.
Essentially, by protecting our producers from import competition we are paying HIGHER prices for Australian food than foreigners are paying for Australian food.
Of course apple growers will whinge, but they will adjust over time, and in reality, their incomes have been protected for a long time anyway.
Warren Buffet supporters in France - the rich want to be taxed more
Quotes -
Graveyard market - buyers don't want in, sellers can't get out (ht: doomsday_trader)
After all, statistics are like bikinis. What they reveal is interesting, but what they conceal is more important (ht: John Booth)
If an Axe is being ground, cluelessness will follow naturally. I used to be an ideologue and as I think back on my unreflective self, I remember that I just chose to devote all my mental energy to what I wanted to believe and none to what I didn't want to believe and the result was I appeared clueless, sometimes intentionally clueless (ht: anon)
The lesson of Alaska is never give away land, even when it is seemingly worthless (ht: M)
Wednesday, August 24, 2011
Gay marriage - questions
The gay marriage debate is extremely interesting. I have a few issues that never seem to be resolved, and are often bypassed in discussion on the matter.
1. Marriage is a religious institution essentially designed to encourage conformity to a norm of one sexual partner, and for specialisation of labour in raising children. Why do so many gay people want to acknowledge this ancient religious anti-gay institution at all? In Australia there are almost no external benefits (in the form of tax treatment, visas, welfare etc) for marriage over de facto relationships. Why not just promise each other you'll be faithful till death do you part? In fact, why do straight people continue to be married (I am, and have my reasons, but I'll keep them for another time).
2. If people want 'marriage equality' why can't I marry my sister? Or my mother? Surely to be equal ALL marriage between consenting adults must be allowed? After all, the main social problems of genetic abnormalities from inbreeding can be solved by IVF - the same way gay couples are having children. In fact, two gay men who happen to be brothers should also be able to marry, no? It is love between two adults, so what's wrong with it? I can't believe anyone could argue for gay marriage and not for sibling marriage, especially between gay siblings, since the arguments are all the same.
3. Any study showing the 'superior' outcomes of children from gay couples (of which there are a few - here's a starting point for some academic research) must control for incomes and other social factors. I have a hard time believing that the 'gay couples with children' sample of society has a similar income distribution to 'heterosexual couples with children' and we know this is a huge factor in child development.
4. Is the desire to have children not in any way related to the desire to mate with the opposite sex? I would have thought that the two are somehow related, which makes me feel like there is more of a 'conforming to social identity' issue at play over the desire to be a progressive gay couple with children.
5. Are children raised by gay parents more or less likely to be gay themselves? It seems intuitive that they would be far more likely, both because one parent would be a biological parent, and the nurturing and exposure to 'gay' behaviour. Is this good or bad? Are children really getting a choice? Will marriage legitimise being gay as normal? Is that a problem?
6. Should gay couples be allowed to adopt children? Why not? Should IVF treatment for lesbian couples be subsidised by Medicare? Surely not. It isn't a medical condition. If they want to pay the full cost for privately provided IVF from a voluntary donor, so be it. If they want to meet a guy at a bar and do it the old-fashioned way, that is fine too. But what about gay male couples? What about married gay brothers? Will recognition of marriage be a stepping stone to more subsidies for gay families?
7. What legal rights exist for the biological parent of the child who is not part of the 'parent couple'? If the relationship breaks down, will the courts decide in favour of the biological gay parent, or the surrogate biological parent? Will marriage affect this decision?
8. If two children from gay family each have one of the parents as biological, and the other parent a different surrogate (so they are not 'blood relations'), can they be married? What about if these two children are gay?
In any case, I always wonder why people don't just say why they feel gay marriage is unacceptable instead of beating around the bush about 'equality'. And those who so strongly support gay marriage should think about the flow-on implications to the role of government, the courts, the rights of parents and health care.
If you can't tell, I see no good reasons in favour of gay marriage, and plenty of unresolved issues surrounding rights of married gay couples, particularly regarding children. Of course, I have no problem with two adults choosing to have a relationship with each other, regardless of their gender.
Tuesday, August 23, 2011
Econompic - negative real interest rates encourage savings
The basic premise behind stimulatory monetary policy is that lower interest rates reduce the cost of debt, and decrease the returns to savings, encouraging present spending and maintaining asset values. But recent experience (particularly in the US) has shown that in a low (or negative) real interest rate environment, savings rates are climbing.
Jake over at Econompic has put forward a reason this might be the case. He argues that if an individual needs to save a certain amount for future consumption, for example someone who wishes to fund their retirement, a low interest rate means they need to SAVE MORE NOW to reach that point.
What surprises me is that Jake’s hypothesis is fairly consistent with Milton Friedman’s permanent income hypothesis, which asserts that people will try and smooth out their earnings over their lifetime (through savings decisions) to maintain a relatively constant level of expenditure. In Friedman’s model, a transitory income, like prize money, would not be spent all at once, but mostly saved and spent over the rest of one’s lifetime. While the reduced debt burden from low interest rates may been seen as temporary by some people and not greatly affect their spending, the reduced return on savings DEFINITELY means that smoothing out income for retirement requires greater levels of saving.
For example, if interest rates are 5%, someone might want to save $1million in order to earn $50,000 per year in returns on which to live during retirement. But if interest rates are 1%, that person needs to save $5million in order to earn $50,000 in returns to fund their retirement.
One might suggest that low interest rates mean that people who need to save will save more, and people who don’t, will save less. This might translate to quite a variation in saving patterns by age, with the soon to retire boomers increasing savings, with the young workers saving less.
The low interest rates and high savings rate correlation probably also has a lot to do with household repairing their balance sheets following massive losses on equities and housing (particularly in the US and the UK).
Over to Jake for the details (original post here).
"At current interest rates, an individual will lose purchasing power in their savings account if there is even an inkling of inflation. A common assumption is that the Fed has done this (i.e. pushed interest rates to historic lows) to increase aggregate demand (i.e. if you are earning nothing, you might as well spend it) or to move investors to riskier investments that might provide better momentum for the underlying economy (i.e. an investment in a corporate bond that makes it cheaper for corporations to borrow).
But what if low to negative interest rates in fact causes the opposite... an increase in the savings rate and derisking by investors? This post is based on a very quick and dirty framework I've been thinking about and focuses on the savings rate, but the same framework could (in my opinion) justify why investors may choose to derisk as well. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
Getting to $100 Saved
Let's assume our saver knows that in ten years they will need to have $100 saved (for retirement, college education for their kids, a new car, etc...). Earning 0% on their savings, they would need to save $10 / year. If they were to earn a rate of return on that $10 saved each year, by the tenth year they would have excess savings (i.e. the blue and yellow lines).
As a result, if an investor can earn more than 0%, they do not need to save $10 / year, but a smaller amount. The chart below shows how much that $10 can be reduced based on various rates of return on their savings.
Assuming the individual earned $200 / year, the original $10 was 5% of their income (i.e. a 5% savings rate). The various amounts needed to save each year is converted to a savings rate below. It clearly shows that if a saver can earn a rate of return greater than 0% (i.e. if interest rates were higher), they can save less to get to their goal.
Unfortunately, savers aren't currently able to earn 0% on their checking / savings accounts. With any inflation, an investors is faced with negative interest rates. So, to get to a $100 real level of savings, an investors will need to save more than the $10 / year.
I know some readers will point out that an individual can always choose to add more risk to increase their returns, but what happens if that investment doesn't work out? An even higher level of savings, which they may not be willing or able to do.
So there's the very basic framework. What am I missing? "
Jake over at Econompic has put forward a reason this might be the case. He argues that if an individual needs to save a certain amount for future consumption, for example someone who wishes to fund their retirement, a low interest rate means they need to SAVE MORE NOW to reach that point.
What surprises me is that Jake’s hypothesis is fairly consistent with Milton Friedman’s permanent income hypothesis, which asserts that people will try and smooth out their earnings over their lifetime (through savings decisions) to maintain a relatively constant level of expenditure. In Friedman’s model, a transitory income, like prize money, would not be spent all at once, but mostly saved and spent over the rest of one’s lifetime. While the reduced debt burden from low interest rates may been seen as temporary by some people and not greatly affect their spending, the reduced return on savings DEFINITELY means that smoothing out income for retirement requires greater levels of saving.
For example, if interest rates are 5%, someone might want to save $1million in order to earn $50,000 per year in returns on which to live during retirement. But if interest rates are 1%, that person needs to save $5million in order to earn $50,000 in returns to fund their retirement.
One might suggest that low interest rates mean that people who need to save will save more, and people who don’t, will save less. This might translate to quite a variation in saving patterns by age, with the soon to retire boomers increasing savings, with the young workers saving less.
The low interest rates and high savings rate correlation probably also has a lot to do with household repairing their balance sheets following massive losses on equities and housing (particularly in the US and the UK).
Over to Jake for the details (original post here).
"At current interest rates, an individual will lose purchasing power in their savings account if there is even an inkling of inflation. A common assumption is that the Fed has done this (i.e. pushed interest rates to historic lows) to increase aggregate demand (i.e. if you are earning nothing, you might as well spend it) or to move investors to riskier investments that might provide better momentum for the underlying economy (i.e. an investment in a corporate bond that makes it cheaper for corporations to borrow).
But what if low to negative interest rates in fact causes the opposite... an increase in the savings rate and derisking by investors? This post is based on a very quick and dirty framework I've been thinking about and focuses on the savings rate, but the same framework could (in my opinion) justify why investors may choose to derisk as well. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
Getting to $100 Saved
Let's assume our saver knows that in ten years they will need to have $100 saved (for retirement, college education for their kids, a new car, etc...). Earning 0% on their savings, they would need to save $10 / year. If they were to earn a rate of return on that $10 saved each year, by the tenth year they would have excess savings (i.e. the blue and yellow lines).
As a result, if an investor can earn more than 0%, they do not need to save $10 / year, but a smaller amount. The chart below shows how much that $10 can be reduced based on various rates of return on their savings.
Assuming the individual earned $200 / year, the original $10 was 5% of their income (i.e. a 5% savings rate). The various amounts needed to save each year is converted to a savings rate below. It clearly shows that if a saver can earn a rate of return greater than 0% (i.e. if interest rates were higher), they can save less to get to their goal.
Unfortunately, savers aren't currently able to earn 0% on their checking / savings accounts. With any inflation, an investors is faced with negative interest rates. So, to get to a $100 real level of savings, an investors will need to save more than the $10 / year.
I know some readers will point out that an individual can always choose to add more risk to increase their returns, but what happens if that investment doesn't work out? An even higher level of savings, which they may not be willing or able to do.
So there's the very basic framework. What am I missing? "
Monday, August 22, 2011
Electric v petrol scooter
I've been reading some great posts recently at Chris Eastwood's blog in my view... . Below is a full post comparing the merits of electric and petrol scooters in a detail rarely seen.
But first a few quotes from Chris that might get you interested in some of the ideas floating around on his blog.
By having an increasingly itinerant population is it any wonder that no one gives a rats arse that your home is being degraded? (here)
I recall a conversation with 2 educators on Fraser Island ... that the last thing you want to do is encourage more people to come to national parks, even if it does somehow liberate more funding from the government it won't pay for the extra damage caused by the extra bogans. (here)
The full electric scooter post is below, and the original link here. Chris finds that the electric scooter produces more greenhouse gas emissions than the petrol version. Please keep in mind the rebound effect, since the electric scooter is so much more expensive (the owner can’t spend that money on other goods).
Over to Chris.
It’s starting to get fashionable to talk about Electric Cars again. The other day I was in at the local scooter shop the other day getting a tyre sorted out for my Yamaha T-Max scooter (and pondering a new 50cc scoot for my wife) when I spotted this electric scooter. So (being an engineering sort of fella) it is exactly in my nature to use this situation to mull over the whole thing (and present it to people who may not have thought about it).
I have been interested in the concept of an electric scooter for a while now but had not really done much research on the topic.
So since it was right in front of me I thought I'd ask some questions, take some pictures and write about it here.
I will say from the start that I like the idea of an electric scooter for city work more than petrol ones for the simple fact that most scooters are 2 strokes, stink and pollute something fierce.
India made a great move when they legislated their nasty "auto" taxis to use CNG rather than the regular 2 stroke ones of the past. Emissions fell and everyone is healthier and happier for it.
Its true that electric engines will need power from the regular power stations, which are in the main coal fired (at least in Australia). However at the very least we move this pollution to a single more efficient generation source (while introducing a number of other inefficiencies in the middle) which can be more controlled and monitored.
Before dribbling on about that too much I thought I'd toss in a comment about the rear drive on the scooter. A brush-less 48Volt 4000Watt hub mounted motor: man that means it can suck 83 amps!! wow
Which makes for some interesting observations about the changes in engineering of the swingarm and frame (because the forces are different now).
The motor can suck up to 4000 watts of energy out of your buttery but of course will only pull as much as is needed for keeping a constant speed when cruising along at a steady speed (say 50Kmh). This is of course exactly like a petrol powered motor, which sucks fuel faster when pulling power than does when cursing along. Interestingly both produce about 4000 Watts of energy (yes, 49cc scooter or electric scooter give you the same power to take off) which should come as no surprise because thats regulated by government.
[aside: to put this sort of tiddly power delivery into perspective, a "vanilla" motorcycle like a Suzuik GS500 has a motor that will deliver at least 38,000 Watts and a timid car like a Ford something like 48,000 Watts of power. So as things go the electric scooter is not pushing the engineering envelope here]
Putting energy in:
People somehow think of petrol as fuel and electricity as energy, I blame our schools for creating this schizophrenic view of reality. The reality is that fuel (petrol, gas) is energy in liquid form. We release that energy by burning it.
Motors turn that energy release into movement. The electric bike stores energy in rechargeable batteries and gets the energy to recharge the battery from your wall socket using something like this:
This little device (which is about the size of a small shoe box) is the charger for the scooter.
To charge your scooter up you have to plug this in to the wall power and into the bike. You cannot really run a long extension lead to it or you will lose power so we meet:
Problem #1 - where can I recharge
If you have your own house and garage you can probably charge it up in your garage, but if you live in an apartment its quite unlikely you have power available where you park your scooter. So you'll need to find a place where you can park it and recharge it: which takes 4 hours. In contrast the regular scooter recharges with fuel at the local servo and takes about 5 minutes to fill and pay for.
So, with fuel being (at the time of writing) about $1.5 a Liter a petrol powered scooter takes about 5L in the tank and will set you back about $7.50 to fill up from dead empty. It’s unlikely you'll run it dry, so you'll probably put in 3L at a time and walk into the servo to pay your $4 bill while grinning at the people who fill up their cars and are paying something like $60 for that.
So what does it cost to "fill up" the Electric scooter?
Well of course electricity costs, in my area right now power you pull out of the wall costs you about 19c per 1000 watts per hour. It’s normally written as Kw/H which seems to confuse people who often profess to not understand their power bill. It’s not all that had to get. Essentially if you plug in and turn on something which uses 1000W (or a kilo watt or 1Kw) and leave it turned on for an hour it cost you 19c.
So how does this apply to the Electric scooter?
Looking at the charger we see that it supplies about 900Watts to the battery. I'm certain it is not 100% efficient so let’s give it some grace and assume that it’s going to pull out 1000Watts of power from your power point in your home (or wherever its plugged into).
So (based on the above rate for power) a 4 hour charge will cost you something less than a dollar, 78c our thereabouts.
According to the information I have on the scooter (which you can verify here) For this princely sum you get to travel 90Km (only under particular conditions).
That is quite attractive. Sounds like its quite positive when reading the basics. So let’s plumb into the ownership and do a little bit of thinking:
Cost comparison
Ok, so 80 cents gets you 90Km on the scooter, but it will of course vary on how you ride and in what conditions. 90Km is of course also the maximum distance, so if you commute across town 25Km you'll not quite get two trips into the one charge (as 50 + 50 will put you out of battery) and you can't stop and top up on the way like you can with a petrol bike. The actual distance you will get may be less depending on factors like:
· hills
· number of traffic lights
· how heavy you are on the throttle on take off (kiss bye bye to fast take offs)
This means that (unless you want to be pushing it home) you'll have to top up every day (fine if you park in a garage in your home, annoying if you have a flat).
So again you'll be plugging in and paying that 80c every day instead of the potential discussed by the maker and seller of the bikes.
If you were to consider a petrol scooter (as a comparison) such as the Honda Scoopy, assuming you get something like 3l / 100Km (and some have suggested you can get 1.4L/100Km) you will pay $4.50 for that 100Km or $2.25 per day. That’s a worst case scenario too, as if you get 1.5L/100km (which is actually likely) then that'll be more like $1.12 for the trip.
Starting to look like much the same running cost as the 80c for the scooter isn't it?
Of course with the petrol version you have the flexibility that you KNOW how much is in your fuel tank, battery charge level is not as accurate and will depend on how cold it is. You can top up your fuel in minutes but need hours (back home where your charger is) to top up the electric scooter.
So this begs the question of how much is the convenience that petrol provides worth to you?
Back on the costs: an acquaintance of mine who has an electric bicycle (less power) recently changed battery from the standard one. How much? Well think in numbers closer to $1000 than $500 and you're on the path.
So unless you're after a battery for one of those tiddly little electric bicycles (with all that implies) you're thinking big money. This starts to lead into the next problem identified for the Electric Scooter and that is:
Problem #2 real operation costs:
Thinking about the above battery example, how long will your rechargeable battery last? Well its only covered by 1 year warranty. So assuming you use the battery optimally (charge and discharge according to the makers ideals) you'll certainly get a year out of it, perhaps two. But are you going to learn to do that or is convenience going to get in the way?
Consider that at the fuel prices of $1.50 /Liter (and before you say that may rise over 2 years ask yourself if power won't) you will get 20,000Km of travel from $450 of petrol.
If you travel 25Km each way to work, thats 50Km per day = 400 days of travel.
Yes, that's right ... your entire year of fuel bill will blown on a battery replacement. Which means in another way of thinking about it, that you are actually costing yourself an extra 80c a trip just for the hell of it when using an electric scooter.
Ok, but we're CO2 free right? That's got to be worth something hasn't it? Well, let me introduce you to ...
Problem #3 - CO2 generation
Its hard to get figures but it seems that (for coal powered stations) about 900g of CO2 is released for every Kw of electricity. So given that the Electric Scooter will need about 4Kw from the wall every day (using the above situational example) it will thus end up generating about 3.6Kg of C02. Of course you could run it to the edge and charge every second day (and push it home occasionally) halving that figure, but that's up to you (and pushing is good exercise).
In comparison burning petrol will release about 625g of C02 for every litre burnt, so assuming you burn 1.5 litres for your 50Km trip you'll generate about a 1Kg of C02 (Note: these calculations are based on figures for C02 in petrol from here)
so yep ... the petrol version generates less CO2 as well. It’s not looking good to me at this point ...
Naturally at this point someone will make the observation that Electric Scooters are at the beginning of their evolution and that petrol engines benefit from decades of development. Well if you have never gone to school or been taught to do any reading you may believe that line.
Let me assure you that both are quite developed technologies.
Petrol motors are actually not significantly advanced compared to 40 years ago (only we've worked on mainly curbing their emissions of other stuff) when you could buy a 70cc Honda Cub (lovely scooter) which used almost exactly the same amount of petrol as the bikes do today.
Then there is the Brushless DC motors used in the scooters, these have been in commercial use since 1886. So its mainly the battery technology which is changed to make storage more compact and perhaps controller circuits to make the motors more flexible. The basic physics of power required to move something hasn't changed between the motor types.
This does not effect the cost and pollution aspects of this calculation (except to say that modern batteries may be a more significant pollution issue than lead acid batterys).
Problem #4 - capital costs
Right now (if you look closely at the first picture) you'll see that an electric scooter equivalent to a 50cc scooter costs about $4250, while a 4 stroke *(more expensive, much cleaner burning less polluting than 2 stroke) Honda Scoopy will cost you about $2500
Yes, you did read that right, you'll pay nearly double for an equivalent electric scooter which will likely produce as much C02 (if that's of interest to you) and certainly more other significant toxic waste than will the choice of a clean 4 stroke petrol powered scooter (compared to 2 stroke motors which are quite dirty creatures).
An excellent document prepared for the Victorian Competition and Efficiency Commission (here) suggests that scooters are more effective people movers than cars are in cities. No surprise there...
To make the case even more for scooters, according to that same report: "A 2000 report (Motorcycle Transport, Powered Two Wheelers in Victoria) by transport researcher, Professor Marcus Wigan, found that motorcycle riders were the only transport mode to indicate no time delays as part of a trip."
There are articles available written to counterpoint this blog post (such as this one) where they suggest that Electric bikes are better than petrol powered ones. It’s worth noting that these are largely written by people who actually sell the electric alternative (but not the electricity).
It’s interesting to note that in the post I cited above the author makes the comparison between a electric bicycle and a postie bike (Honda CT110). The CT110 is a work horse, it'll carry another 40kg of mail and still accelerate and travel at 60Kmh if you desire, but the author makes a disingenuous comparison with an electric bicycle (which only carries you and you have to pedal too) comes out on top (when he ignores the battery issue). Yet the bicycle has a motor which wouldn't have enough power to pull the skin of a custard when compared to a postie bike ... gosh, bet that'll be popular on the farm!
But what about Solar charging? That would be CO2 free...
Well that's a good point. If you were to get a 1.5 Kw system it would likely produce enough energy on a good day to charge your scooter (if you left it at home) within 5 hours (you don't get 1.5Kw all the time out of them, ask someone who owns one). So for the additional investment of $2500 (around about and you won't be back feeding the grid while your charging) you can be comfortable in the knowledge that you won't pay that extra 80c a day (but you'll still pay the other costs)
So that's $4200 for the scooter, and $2500 for the solar charger system (no rebate on that one) taking your investment to $6700 for a system which needs you to leave the bike home during the day for charging ... sounds great to you too?
So in summary:
It seems like the following to me
· I will save a little per trip (about 80c for a 50Km trip vs $1.25)
· but I pay double to purchase ($4200 vs $2500)
· unknown depreciation losses (but it’s fair to say you can't lose more than $2500 on the petrol scooter)
· pay more for operational costs (the battery will die)
· actually create more pollution in almost every way by using an electric scooter over a petrol one.
· You have to be able to park it where you can charge it (in a secure place or risk getting your charger stolen)
· if your running low in power on the way home you cannot just stop in to a servo to top up.
Why are you buying the scooter? Economy? Environmentally friendly?
The bottom line is if you want to be really environmentally friendly, go get a 50cc to 110cc 4 stroke scooter stop driving your car and help save the world’s atmosphere and resources.
Sunday, August 21, 2011
Economies of scale do not equal productivity
 Only three things matter in the Australian economy - productivity (how much each person produces); employment (how many people are producing); and equality (how that output is shared). All the other random shrapnel of economic news that flies around is kind of irrelevant.
Only three things matter in the Australian economy - productivity (how much each person produces); employment (how many people are producing); and equality (how that output is shared). All the other random shrapnel of economic news that flies around is kind of irrelevant.(c/o Andrew Charlton + must read article entitled The Economic Myths of Peter Costello here)
Productivity is the key to greater wealth, as an individual, a nation, and a world. Productivity is doing more with less. It is that simple. Unfortunately people often equate productivity with economies of scale and population growth, which leads to a poor understanding how economic growth really occurs.
If a farmer selectively breeds his crop so that the next generation of plants yield 5% more grain, with no further inputs required (no more water, fertiliser, harvesting time etc), then he has made a 5% productivity improvement. The output in terms of grain is 5% higher for the same inputs.
Productivity gains flow through the economy, allowing us to produce more goods over time. When other farmers follow this lead, we find that marginal land can now be used productively. We find that fewer people need to work in agriculture, because each farmer is producing more food. This frees up labour to be employed elsewhere in the economy, producing other goods to satisfy our desires.
Productivity gains normally come from two sources. The first is in the form of new inventions and innovations in the methods of production - a new engine design, a new breed of plant, a new manufacturing technique or a new material. Innovation in the methods of production is THE key driver of our prosperity.
A second way that productivity improves is through economies of scale. Even in the absence of new technology or innovation, we can produce more output with less input by specialisation of labour, and larger and more efficient capital equipment, to achieve economies of scale.
However, people often get the drivers of productivity confused. They believe economies of scale are the main driver, and innovation is some secondary consideration. But in fact, economies of scale are only sometimes productivity enhancing. Often there are diseconomies of scale, where there is a trade-off between the size of the economy, and the efficiency of the economy. This occurs when the marginal cost of production is higher than the average cost (which is bizarrely where economists believe production usually exists on the cost curve except in the case of a natural monopoly).
For example, urban water supply can initially be produced very cheaply with a network of local dams. However, once local water needs exceed this amount, another source must be found. In Brisbane and Melbourne, this source is desalinised sea water, which is far more costly than any other water. What this means is that the cost of the last batch of water from the desalination plant (the marginal cost) is far higher than the existing average cost of water to the city, which increases the average cost and makes all water more expensive. Businesses that use water will pay more, and that leaves them less able to increase production and invest in their own innovative capital. Households pay more for water, leaving them less income to spend on other goods. We are all worse off, and far less productive, due to this diseconomy of scale in water supply.
There are many other examples from roads, to electricity, to housing.
Another popular view is that there is a connection between the population of a city or country, economies of scale, and productivity - if we don’t have more people, we can’t get the economies of scale necessary to become more productive.
Yet the great problem with this view is that economies of scale do not rely on the population of the geographical area where goods are produced, but on the size of the market being satisfied by that production. This is why German car manufactures in a single Länder (state), with a population of perhaps 10 million, can achieve greater economies of scale than many other manufactures because they supply a global market with a high volume of vehicles. More people in these Länders will do nothing to make these auto firms more productive, and may likely achieve the opposite effect if the required expansion of the housing stock, roads and other infrastructure, competes for labour demand and finance with the car manufactures.
Even if population growth means that expansion of some of our capital stock occurs where economies of scale exist, there is always the need to expand the housing stock – a capital good where economies of scale do not readily exist. Duplicating any capital in this nature comes at a cost to society that can never be recovered. Read more on that here.
The below Venn diagram shows the relationship between these factors and productivity. As you can see, innovation in new production technology is the primary driver, with economies of scale sometime being beneficial for productivity, and population growth usually coming at a cost to productivity.
The implication then is for government especially to be aware of when expansion of publicly funded capital is approaching diseconomies of scale and recognise this cost to society. Why stimulate population growth when it comes at a cost to the existing population in the form of more expensive water, transport, and the diversion of resources from genuine productive investment?
Thursday, August 18, 2011
Friday thoughts
Democracy
In a democracy, we put political power into the hands of some and try to limit the damage they will do as much as we can by putting all the obstacles we can think of in their way while giving them the authority to do what needs to be done. (from here)
Warren Buffet says tax me more.
OUR leaders have asked for “shared sacrifice.” But when they did the asking, they spared me. I checked with my mega-rich friends to learn what pain they were expecting. They, too, were left untouched.
While the poor and middle class fight for us in Afghanistan, and while most Americans struggle to make ends meet, we mega-rich continue to get our extraordinary tax breaks. ...Last year my federal tax bill — the income tax I paid, as well as payroll taxes paid by me and on my behalf — was $6,938,744. That sounds like a lot of money. But what I paid was only 17.4 percent of my taxable income — and that’s actually a lower percentage than was paid by any of the other 20 people in our office. Their tax burdens ranged from 33 percent to 41 percent and averaged 36 percent.
...Back in the 1980s and 1990s, tax rates for the rich were far higher, and my percentage rate was in the middle of the pack. According to a theory I sometimes hear, I should have thrown a fit and refused to invest because of the elevated tax rates on capital gains and dividends.
I didn’t refuse, nor did others. I have worked with investors for 60 years and I have yet to see anyone — not even when capital gains rates were 39.9 percent in 1976-77 — shy away from a sensible investment because of the tax rate on the potential gain. People invest to make money, and potential taxes have never scared them off.
...I know well many of the mega-rich and, by and large, they are very decent people. They love America and appreciate the opportunity this country has given them. Many have joined the Giving Pledge, promising to give most of their wealth to philanthropy. Most wouldn’t mind being told to pay more in taxes as well, particularly when so many of their fellow citizens are truly suffering.
...I would leave rates for 99.7 percent of taxpayers unchanged and continue the current 2-percentage-point reduction in the employee contribution to the payroll tax. This cut helps the poor and the middle class, who need every break they can get.
But for those making more than $1 million — there were 236,883 such households in 2009 — I would raise rates immediately on taxable income in excess of $1 million, including, of course, dividends and capital gains. And for those who make $10 million or more — there were 8,274 in 2009 — I would suggest an additional increase in rate.
But he can make a voluntary contribution of taxes the US government at any time. So why doesn’t he? As a friend recently suggested, he is trying to leverage his good will by forcing others to come for the ride. But he also states that his fellow mega-rich friends are "very decent people" and "give most of their wealth to philanthropy" and "wouldn't mind being told to pay more in taxes". My questions are
Why isn't a greater tax contribution part of their philanthropy?
What is stopping them?
Do they feel that giving privately to charity offers more social gains on a per dollar basis?
If they were taxed more, would they give less to these charities?
Rebuilding the US Economy: Part 2, Real Job Creation
Creating Value
In Chapter One of my book, Organizational Economics: The Formation of Wealth, and in a post entitled Concept of Value, I discuss three types of value, knowledge, capacity, and political. I will trust that the readers of this post have read one or the other [or both? :-)].
In my book I argue that, in general, governments (and governance) cannot create value, in terms of ROI. Instead, governments have two interlocking roles; Creating the policies and standards (see my post The Purpose of Laws, Regulations, Policies, and Standards and Standards: A Mission of Government) and Governance that reduce Intra- and Inter-organizational friction and Creating the environment or context in which value can be created. This involves that construction and maintenance of defense (see my Post: Security: A Mission of Government), and formal and fair markets, transportation, utilities, and communications systems(See my Post: Infrastructure: A Mission of Government and Organizational Control).
Creating Jobs
In my book I argue that, in general, governments (and governance) cannot create value, in terms of ROI. Instead, governments have two interlocking roles; Creating the policies and standards (see my post The Purpose of Laws, Regulations, Policies, and Standards and Standards: A Mission of Government) and Governance that reduce Intra- and Inter-organizational friction and Creating the environment or context in which value can be created. This involves that construction and maintenance of defense (see my Post: Security: A Mission of Government), and formal and fair markets, transportation, utilities, and communications systems(See my Post: Infrastructure: A Mission of Government and Organizational Control).
Creating Jobs
Currently, leaders of many nations are claiming they know how to create job others are struggling to determine how to do this. Unfortunately, governments cannot create value, and since they cannot create value they cannot create jobs, as such; they can only create the context in which job creation is possible (this creates Value On Investment and the private sector can turn into ROI).
In the US, the Leadership in the period from 1933 to 1963 understood this. This is the period in which the United States spent the most on creating the infrastructure necessary for job creation. Examples include in the 1940s the TVA, the Hoover Dam, rural electrification, the national road systems (built by the WPA) and so on, enabled the industries of WWII to support, and some would argue to win the war. In the 1950s, the Interstate Highway System. All of this enabled the growing economy from the 1950s to the late 1960s. In the early 1960s NASA's Man to the Moon program built the Internet and other technologies of the 1990s, which again, helped the economic growth of the 1980s to 1990s.
However, starting with Johnson and the entitlement programs, the US lost its way, living for 45 years on what was built up prior. Instead of concentrating on infrastructure spending, the Johnson and succeeding administrations have concentrated on spending on a "social safety net". Politicians have found this to be a much better way to get reelected. And, in effect, this is creating exploitive political value from the knowledgeable by the ignorant (see Concept of Value or my book, Organizational Economics: The Formation of Wealth for the definition of exploitive political value). I suspect that most everyone would agree, now, that having a job is the best "social safety net". And that spending resources on the infrastructure is the only Mission that a government has to help to create jobs.
The second arrow that a government has in its quiver is its laws, regulations, policies, and standards. The executive and legislative branches of government at the federal and state level all operate on the secondary road maintenance process. This is the process whereby county road departments fix or repair the roads. After a road has been paved it always require maintenance due to use and the weather. Initially, as road deteriorate, the first cracks and potholes appear, crews are sent out to patch them. Then, as potholes appear in the potholes and the cracks open up again, the crews come back. At some point the patches on the roughness caused by cracks and potholes make it impossible for the normal use. When the citizens finally scream loudly enough, the road commission will send crews to "top coat" or pave over the entire surface. Generally, this is enough to quiet the outcry, but within a year the potholes and cracks with start to reappear. This restarts the maintenance (patching) cycle.
The US Congress and the various state legislatures attempt to use this process, also known as the "duct tape" process, to adjust or repair the laws, regulations, policies, and standards to support their Mission. Since, at least in the US, there are two very distinct political camps with respect to the Federal Governments Mission. One is the Keynesian "demand-siders" who say that putting government money (our money) into the hands of the "have-nots" will stimulate the system into growing jobs. What has been found is that most people were burned by having too much credit and are taking the money to pay off debts and to save for the future. One the other side are the "supply-siders" who say that governments ought to get out of the way (deregulate) and let business do its job of creating jobs. This was tried in the 1990s and led to the bubbles of the 2000s and the bust of 2008.
Neither side realizes (or wants to realize) that supply and demand are all functions of a (mostly) closed loop system (as is the chicken or egg problem and many others). Further, neither side wants to realize that there are only two ways to create jobs within any organization. The first is through some stimulus external to the organization and the second is through the growth of knowledge.
In the 1930s, President Roosevelt enacted a series of "New Deal" programs. These "demand-sider" programs, like the CCC, the WPA, and the TVA were designed to create jobs, pure and simple. Fortunately for the country, these programs were also creating an entire country-wide economic infrastructure, that is they were creating Value On Investment (VOI). Additionally, they started to lift the country out of the Great Depression. But this was an artificial lift. When the various programs were challenged and court and found to be unconstitutional in the mid-1930s, by 1937 the country went into recession.
In 1938, Brig. Gen. George C. Marshall was named Deputy Chief of Staff for the Army. He was appalled at the state of the forces. The United States had the 17th largest military in the world and was using WWI weapons that were leftover from the buildup in 1918. With his low key approach, honesty, and a doctrine of preparedness (and the onset of WWI in Europe), by 1939, when he became Chief of Staff, Congress that had been wrangling about million dollar items started to provide first hundreds of millions and then billions of dollars for the Army (which include the Air Force) and the Navy. Initially, this was for new weapons. But the manufacturing of these new weapons required new factories and new tooling.
Very quickly the US economy bounced back and then moved out smartly. Companies, who had never paid attention to military contracts (and many of whose leaders were isolationists) were now drawn to these contracts like yellow jackets to a picnic. "Suddenly", new construction and manufacturing jobs opened up and unemployment fell, hard (in fact so hard, that during WWII, women were first employed in large numbers). Where Dr. "New Deal" (demand-sider) could not cure the jobs issue, Dr. WWII did.
In the process of up-dating the weapons, a great deal of research and development were done on both sides of the conflict. The results included much more reliable radios, rockets (the V-2 led to the Moon rocket Apollo, (see my post The Cost of Rockets Built by NASA: Waterfall Process vs Short-cycle and Agile Processes), the computer, and the Atomic Bomb. And all of these supported new businesses with new jobs after the war.
However, somewhat inadvertently, the United States government continued to support job creation in the 1950 and early 1960s through their support of basic research in nuclear physics, space, and military aircraft. However, with the Johnson administration and succeeding administrations, all of this work was killed off in favor of "buy the votes" entitlement programs. Now with a crumbling infrastructure and little real research and development, and little support for education or educational reforms (built on a good Enterprise Architecture Framework), all of the politicians are falling back on either demand-side or supply-side economic processes to create jobs; and neither will.
The common ground is the need for jobs. And the only way is to straighten out the law, regulation, policies and standards "cluster-blub", cut entitlements, re-start programs like the super collider (and others of this type), and to create an education enterprise architecture that recognizes difference in the ways teachers teach and students learn, and which teaching methods are best for which students (plus making the central supervisor's office much more cost efficient).
[Sidebar: That is not to say that there are not people that deserve some help, though I suspect that between charitable organizations and good governmental regulation most of these people could be taken care of.]
Notice that it takes about 25 to 30 years (a generation) from the government investment until the investment truly bare full fruit. It is very silly of the politicians and people of countries to expect it in less than a full generation. However, in a recent interview, one retired US Department of Transportation head indicated that politicians cannot stand that when they appropriate a trillion dollars to upgrade highways, it takes at least 2 years to spend the funds--to me that seems way too short a time. But the politicians (and their constituents) are of the instant gratification type and expect that 9 women can make a baby in a month.
My contention is that if we don't follow the plan outlined here, the US will continue on its merry way, until, like the economy in Ayn Rand's novel "Atlas Shrugged", it hits a discontinuity and falls into complete chaos.
In the US, the Leadership in the period from 1933 to 1963 understood this. This is the period in which the United States spent the most on creating the infrastructure necessary for job creation. Examples include in the 1940s the TVA, the Hoover Dam, rural electrification, the national road systems (built by the WPA) and so on, enabled the industries of WWII to support, and some would argue to win the war. In the 1950s, the Interstate Highway System. All of this enabled the growing economy from the 1950s to the late 1960s. In the early 1960s NASA's Man to the Moon program built the Internet and other technologies of the 1990s, which again, helped the economic growth of the 1980s to 1990s.
However, starting with Johnson and the entitlement programs, the US lost its way, living for 45 years on what was built up prior. Instead of concentrating on infrastructure spending, the Johnson and succeeding administrations have concentrated on spending on a "social safety net". Politicians have found this to be a much better way to get reelected. And, in effect, this is creating exploitive political value from the knowledgeable by the ignorant (see Concept of Value or my book, Organizational Economics: The Formation of Wealth for the definition of exploitive political value). I suspect that most everyone would agree, now, that having a job is the best "social safety net". And that spending resources on the infrastructure is the only Mission that a government has to help to create jobs.
The second arrow that a government has in its quiver is its laws, regulations, policies, and standards. The executive and legislative branches of government at the federal and state level all operate on the secondary road maintenance process. This is the process whereby county road departments fix or repair the roads. After a road has been paved it always require maintenance due to use and the weather. Initially, as road deteriorate, the first cracks and potholes appear, crews are sent out to patch them. Then, as potholes appear in the potholes and the cracks open up again, the crews come back. At some point the patches on the roughness caused by cracks and potholes make it impossible for the normal use. When the citizens finally scream loudly enough, the road commission will send crews to "top coat" or pave over the entire surface. Generally, this is enough to quiet the outcry, but within a year the potholes and cracks with start to reappear. This restarts the maintenance (patching) cycle.
The US Congress and the various state legislatures attempt to use this process, also known as the "duct tape" process, to adjust or repair the laws, regulations, policies, and standards to support their Mission. Since, at least in the US, there are two very distinct political camps with respect to the Federal Governments Mission. One is the Keynesian "demand-siders" who say that putting government money (our money) into the hands of the "have-nots" will stimulate the system into growing jobs. What has been found is that most people were burned by having too much credit and are taking the money to pay off debts and to save for the future. One the other side are the "supply-siders" who say that governments ought to get out of the way (deregulate) and let business do its job of creating jobs. This was tried in the 1990s and led to the bubbles of the 2000s and the bust of 2008.
Neither side realizes (or wants to realize) that supply and demand are all functions of a (mostly) closed loop system (as is the chicken or egg problem and many others). Further, neither side wants to realize that there are only two ways to create jobs within any organization. The first is through some stimulus external to the organization and the second is through the growth of knowledge.
In the 1930s, President Roosevelt enacted a series of "New Deal" programs. These "demand-sider" programs, like the CCC, the WPA, and the TVA were designed to create jobs, pure and simple. Fortunately for the country, these programs were also creating an entire country-wide economic infrastructure, that is they were creating Value On Investment (VOI). Additionally, they started to lift the country out of the Great Depression. But this was an artificial lift. When the various programs were challenged and court and found to be unconstitutional in the mid-1930s, by 1937 the country went into recession.
In 1938, Brig. Gen. George C. Marshall was named Deputy Chief of Staff for the Army. He was appalled at the state of the forces. The United States had the 17th largest military in the world and was using WWI weapons that were leftover from the buildup in 1918. With his low key approach, honesty, and a doctrine of preparedness (and the onset of WWI in Europe), by 1939, when he became Chief of Staff, Congress that had been wrangling about million dollar items started to provide first hundreds of millions and then billions of dollars for the Army (which include the Air Force) and the Navy. Initially, this was for new weapons. But the manufacturing of these new weapons required new factories and new tooling.
Very quickly the US economy bounced back and then moved out smartly. Companies, who had never paid attention to military contracts (and many of whose leaders were isolationists) were now drawn to these contracts like yellow jackets to a picnic. "Suddenly", new construction and manufacturing jobs opened up and unemployment fell, hard (in fact so hard, that during WWII, women were first employed in large numbers). Where Dr. "New Deal" (demand-sider) could not cure the jobs issue, Dr. WWII did.
In the process of up-dating the weapons, a great deal of research and development were done on both sides of the conflict. The results included much more reliable radios, rockets (the V-2 led to the Moon rocket Apollo, (see my post The Cost of Rockets Built by NASA: Waterfall Process vs Short-cycle and Agile Processes), the computer, and the Atomic Bomb. And all of these supported new businesses with new jobs after the war.
However, somewhat inadvertently, the United States government continued to support job creation in the 1950 and early 1960s through their support of basic research in nuclear physics, space, and military aircraft. However, with the Johnson administration and succeeding administrations, all of this work was killed off in favor of "buy the votes" entitlement programs. Now with a crumbling infrastructure and little real research and development, and little support for education or educational reforms (built on a good Enterprise Architecture Framework), all of the politicians are falling back on either demand-side or supply-side economic processes to create jobs; and neither will.
The common ground is the need for jobs. And the only way is to straighten out the law, regulation, policies and standards "cluster-blub", cut entitlements, re-start programs like the super collider (and others of this type), and to create an education enterprise architecture that recognizes difference in the ways teachers teach and students learn, and which teaching methods are best for which students (plus making the central supervisor's office much more cost efficient).
[Sidebar: That is not to say that there are not people that deserve some help, though I suspect that between charitable organizations and good governmental regulation most of these people could be taken care of.]
Notice that it takes about 25 to 30 years (a generation) from the government investment until the investment truly bare full fruit. It is very silly of the politicians and people of countries to expect it in less than a full generation. However, in a recent interview, one retired US Department of Transportation head indicated that politicians cannot stand that when they appropriate a trillion dollars to upgrade highways, it takes at least 2 years to spend the funds--to me that seems way too short a time. But the politicians (and their constituents) are of the instant gratification type and expect that 9 women can make a baby in a month.
My contention is that if we don't follow the plan outlined here, the US will continue on its merry way, until, like the economy in Ayn Rand's novel "Atlas Shrugged", it hits a discontinuity and falls into complete chaos.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)